Tip 1: The Nation as a Cultural Community
Tip 1: The Nation as a Cultural Community
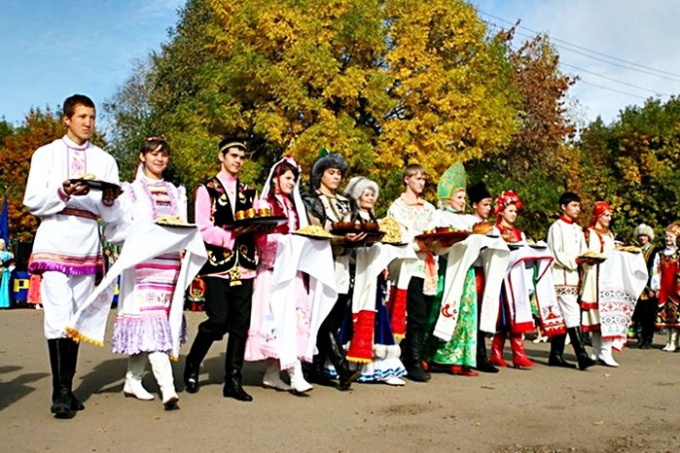
The cultural community to which each nation is associated is the guarantee of spiritual cohesion and unity. However, in a negative way, national culturalism can engender ethnic discrimination.

Herder's concept
The founder of the concept of the nation as a culturalLutheran priest Herder, who was keen on the works of Kant, Rousseau and Montesquieu, became a community. In accordance with its conception, the nation was an organic group, having its own language and culture. This concept formed the basis of the history of culture and laid the foundation of cultural nationalism, where the most important postulate was the value of national culture. The most important feature of the nation, Herder considered language. In turn, language generated a distinct culture, expressed in legends, national songs and rituals. Statehood here receded into the background, and the most important value was given to collective memory and national traditions. The main idea of Herder's works was the definition of a nation as a natural community that originated from ancient times. Modern psychologists confirm this concept, because for its security, people are inclined to form groups, which include many people close in spirit and culture.The development of national culture
In 1983 Ernest Gelner in his work describedthe connection of nationalism with modernization. Earlier, in the pre-capitalist era, nations were bound by various bonds, the main ones of which were cultural. During the period of industrialization, social mobility became more important, and nationalism became the ideology of preserving cultural unity. Ethnos carry out the primary task - consolidation of social ties between people belonging to one historically formed community. The sense of national unity here is fundamental, therefore, such social groups are sufficiently stable and spiritually united. However, the desire for ethnic and cultural self-determination can be accompanied by a manifestation of aggressiveness, intolerance and discrimination against other ethnic groups. Cultural nationalism, at its best, enriches world culture, preserving the traditions of its ancestors, serves as a basis for the development of ethnic groups. The nation as a cultural community will always influence the political situation. In multinational countries, the possibility of disagreement increases against the background of national and cultural differences. Therefore, the state should become a unifying and deterrent factor for preventing negative processes in interethnic relations.Tip 2: What is a nation?
Nation Is a community of people united by spiritual, socio-economic and cultural-political ties. The Latin word natio in translation means "tribe, people".
Instructions
1
In the system of international law the term "nation"the state is synonymous with the concept. From the political point of view, the nation is called people who uniformly position themselves in space and time, link their existence to a certain territory and history of development. This self-positioning must be stable and conscious.
2
Also stands out such a notion as ethnonation. This word denotes the ethnos, which as a result of historical development has reached the national level, that is, it refers to a certain state, has political institutions and is aware of its citizenship. From the ethnonations it is necessary to distinguish mono-national states, in which there are equal national minorities. Ethnonality, on the other hand, has a genetic and anthropological unity.
3
Often the nationality is confused with the nation. However, the second concept denotes an ethnic community, and this is only one of the characteristics of a nation. Therefore, the concept of nationality is narrower.
4
The composition of the nation is divided into monoethnic and polyethnic. Monoethnic are rare, more often a nation is formed on the basis of several ethnic groups.
5
Representatives of one nation can be combined withpoint of view of the language, but this is also not an obligatory condition. The same language can be used by several nations. In the composition of polyethnic nations, most ethnic groups can use a non-native language for them or do not know the language of their nation.
6
Historically, the formation of nations was associated withthe development of production relations, a common economic system, and the commercial sphere. As a consequence, a need arose to overcome national fragmentation and self-isolation. Moreover, nations were formed both on the basis of large nationalities with established ties, and in the absence of all the necessary conditions (in the course of colonial battles, wars for independence).
7
According to the researcher of nationalism B. Anderson, the first modern nations were Latin American. The very concept of a nation in the political sense appeared during the Great French Revolution. The youngest nations are Vietnamese and Cambodian.
Council 3: Nation as a subject of politics
The nation is one of the most important subjectspoliticians. The national question is given considerable attention in the political programs of parties, regardless of their spectrum. Nations are often the initiators of political change.

The term "nation" has a different interpretation. It can denote the population of the country (either the state itself) and the ethnic community. Modern understanding of the nation was formed during the Great French Revolution, when national self-consciousness began to form. The French revolutionaries described themselves as patriots, respectively, it was the civil identity that formed the basis for the formation of the nation. Since then, the nation is understood as a historically formed community of people based on the economy, language, territory and psychology, as well as the characteristics of culture. Some scholars believe that nations can not be considered real subjects of political processes. In their opinion, nations are artificially constructed by the political elites of education, limited within the state. However, one can hardly agree with such a position. Since the national aspect is often the basis of the requirements for the state. It was the national idea that became the dominant force for activating movements against oppression and slavery, the formation of national states. In modern political life, national problems play an important role. Among them, sovereign development, equality of nations, inalienable rights of nations (for self-determination, for self-identification, etc.). National issues can contribute to an increase in the level of political participation, they play a significant role in the party struggle, in the process of forming political institutions. Nations can contribute to the solution of other important socio-political tasks. In particular, they can contribute to raising the cultural level of a particular nation, or their social security. Other likely goals of national movements are the spread of national identity (for example, by opening schools with instruction in the national language), extending the rights to special forms of political representation, and legislative initiatives. There is even a separate ideology - nationalism, the keynote of which is the protection of the interests of national communities in interaction with the state power. This ideology is activated in difficult moments of the historical development of the state, when it is necessary to ensure high cohesion of society and its constituent parts. Sometimes nationalism can take on an extreme form, which defends the thesis of the superiority of one nation over another. Nations are both subjects and objects of politics. However, the role of nations is not the same. Proceeding from the position they occupy, the nations dominate and oppressed. The former possess the full range of political resources. When realizing their political goals, they can rely on the army, state bodies, the media, etc. Oppressed nations act as subjects of politics, as they oppose the dominant nations. Ignoring their interests can lead to serious negative consequences for the stability of society. National and interethnic relations do not exist in a pure form. Within the nations there are different social strata and groups, which makes them closely interrelated with political and economic aspects. The importance of nations in political life is conditioned by the fact that many politicians and movements use the national question as their trump card in the political struggle.
Tip 4: What is ethnos and ethnic group
The term ethnic group has a large numbervalues. It is used by ethnologists, sociologists, political scientists, geographers and many other scientific figures. The reason for such popularity is the capacity of the concept and the abundance of its components.

Many argue that for the correctdefinitions of terms, ethnos and ethnic group, it is necessary to take into account the fact that there are ethnic groups created artificially in the form of uniting people by conviction, but there are natural ethnic groups that are created by their own convictions and those that are formed under the influence of some group.
In ethnology
In ethnology, the term ethnic group is identicalthe concept of subethnos: an ethnic group, allocated on a regional basis, but having cultural, linguistic and other characteristics distinct from the local population. Such groups are characterized by their own self-awareness.
In sociology
To date, one of the mostcommon values of an ethnic group is the totality of people of one nationality, which are localized not on their historical territory, but on the territory of other peoples, in other states (not the titular nation). In this case, the number of members of an ethnic group can be determined by hundreds, thousands or even millions. As a rule, the members of the ethnic group settle as closely as possible (typical example: Chinatown, reservations, etc.). At the same time, all the members of the ethnic group are united not by political and territorial features, but by one language, culture and traditions.
In many countries of the world such ethnic groups are a recognized public minority. They are for various reasons separated from their ethnos and forced to conduct their life outside of it.
In political science
In some cases, the term ethnic groupis defined as the union of several ethnic groups according to certain criteria. Usually they have a similar racial origin. Closely related peoples can belong to one ethnic group. One example is the ethnic group of the ancient Slavs or Germans.
Ethnos
The ethnic group has a largenumber of values. It is more extensive than the concept of ethnos. Many scientists try to give a precise definition of the last term, but it has the property of changing its value, which depends on the type of community it is applied to.







