Tip 1: All about squamous cell carcinoma
Tip 1: All about squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is a type of cancerSkin, it is also called light. In general, it is less aggressive than melanoma - a "black" type of skin tumor, but this is no less dangerous. The thing is that squamous cell carcinoma is able to remain unnoticed for a very long time.

"Light Cancer" occurs about 10 times more often,than an aggressive black version. The main cause for its appearance, it is believed the ultraviolet radiation, it appears, usually on the places of the skin, which are usually open sunlight, for example, on the head, on the face or on the outside of the hand. Nevertheless, physicians are cases of detection of squamous formations and in the most unexpected places, such as mucous membranes of the mouth or on the tongue.
Causes
The older the person, the higher for him becomesRisk of disease. In addition to the genetic predisposition to this kind of oncology, during the course of life, various kinds of dermatitis, keratoses, papillomaviruses are added to it, which can give impetus to the development of the disease. Also to the risk factor can be attributed and various skin lesions, after the healing of which there are scars.Symptoms
Regardless of what exactly was causedappearance of the disease, squamous cell carcinoma begins always the same. On the skin appears a red spot with a peeling surface, which begins to grow and shows no desire for spontaneous healing. Over time, the tumor develops only in the upper layer of the epidermis, it can only rise slightly above its surface, but eventually it becomes an ulcer and can germinate into nearby tissues.Treatment
The treatment of squamous cell carcinoma is highly dependent onAt what stage the disease was detected. The simplest therapy is the so-called pre-cancer, or actinic keratosis, which in itself is not cancer, but with a very high probability of it sooner or later becomes. It can be removed by cauterizing with liquid nitrogen, surgical intervention, or by lubricating the formation with a special fluorouracil cream that can destroy rapidly growing skin cells. Removal of the formation can also be performed with the help of a laser, while the skin can have rather deep scars, but at the same time this method can get rid of squamous cell cancer with a probability of almost 100%. If, however, a recurrence occurs, it usually occurs within 3-6 months of the operation.Prevention
Prophylaxis of squamous cell cancer is quiteit is necessary not to abuse stay in the sun. When entering the street, you should hide the exposed areas of the skin under the clothes or lubricate them with sunscreen. And without fail, immediately consult a doctor if a strange formation is found on the skin, regardless of the location of the site. In general, the chances of cure for squamous cell cancer are extremely high.Tip 2: What is squamous cell cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor that develops in a place with a flat epithelium. It is treated with the help of electrocoagulation, chemotherapy, cryodestruction, laser, etc.

Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor,which can be formed in any organ where there is a flat epithelium. This can be the esophagus, the oral cavity, the cervix, as well as the lungs, the larynx, the whole skin, etc. Squamous cell carcinoma is less common in cancer of other organs, it is often this form of the disease that leads to death. Among the white population, people with lighter skin are more often ill. Insects do not play any role in Asians and African Americans, and cancer develops under the influence of other factors.
Causes and Symptoms
The causes of the disease can be keratosis, especially inOld age, long unhealed wounds, burns and inflammations. If the patient suffered from pigment xeroderma or x-ray dermatitis, he could also develop such a form of cancer. The human papilloma virus, complicated by the influence of carcinogenic factors, often provokes the development of skin cancer. Symptoms of the disease: - formation on the skin, having the form of a tumor, gradually increasing in size and having the appearance of an unhealed ulcer; - often such an ulcer oozes with an unpleasant odor; - the scar can grow, crack, bleed and acquire a more dense structure; - the plaque present on the skin does not disappear for a long time and gradually increases; - Regional lymph nodes increase.Diagnosis and treatment
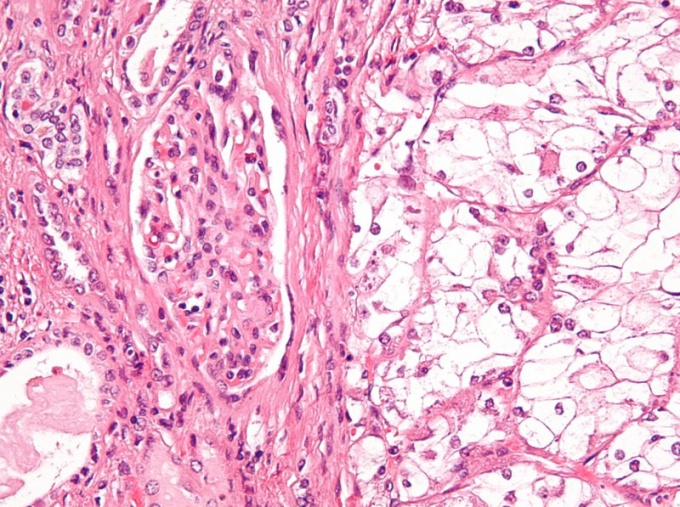
Diagnosing this disease is not difficult, because. The pathological focus is visible to the naked eye. In addition to general examination, the doctor takes a tissue sample from the outbreak to study under a microscope and determine whether this tumor is a squamous cell carcinoma or a different disease. X-rays, MRI, CT, etc. are used to detect metastases. Squamous cell cancer is treated with the following methods: - surgical removal of the tumor; - electrocoagulation. Cancer cells are exposed to an electric current of a special frequency, leading to their destruction; - cryodestruction. This method involves exposing cancer cells to extremely low temperatures; - photodynamic therapy; - Chemotherapy; - laser treatment; - exposure to the tumor with X-rays, which destroys malignant cells. The method of treatment is chosen individually, depending on the stage of the disease, the localization of cancer and the size of the focus.Tip 3: How does cancer of the lips look?
Lip cancer is a malignant tumor that is formed from the skin of the red border of the upper and lower lips. This disease is preceded by various precancerous conditions.

Causes of development and prevalence of cancer of the lip
Lower lip cancer occurs quite often. Among 100 thousand people four have this disease. Most often, this disease affects men. Analyzing the geographical distribution of the disease, it can be noted that the highest incidence rate is observed among the rural population in comparison with the city population. The main factors that contribute to the development of lower lip cancer include the following: alcohol consumption, smoking, unsatisfactory teeth condition (caries, inappropriate Orthopedic structures in the oral cavity, the presence of dental calculi, bite anomalies), ultraviolet irradiation. Among harmful industrial factors, one can note industrial dust in the textile, leather and coal industries, as well as contact with petroleum products. To the previous cancer of the lip diseases include warty papillomatosis of the red border of the lower lip, leukoplakia and keratoacanthoma, limited precancerous hyperkeratosis, cheilitis of various genesis and cutaneous horn. Pre-cancerous diseases can be diffuse or focal. Treatment of diffuse processes is performed by a dentist. In turn, focal diseases require surgical intervention, for example, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The cancer of the lower lip is usually located on the red border of the lip, away from the middle line, in rare cases in the corners of the mouth. Even more rare is the cancer of the upper lip. According to the structure of the tissue that forms the tumor, the cancer of the lip is referred to the squamous keratinizing form of the oncological disease. Metastasis in this case usually occurs in the lymphogenous way into the chin, deep cervical, parotid, submandibular lymph nodes. Since there is a connection between the lymph nodes through the lymphatic vessels, there is often a two-sided metastasis. Very rarely with squamous nonkeratinized lip cancer, this process can begin in internal organs.Diagnosis and treatment of cancer of the lips
Diagnosis of lip cancer is not difficult,Since the lesion is available for examination already in the early stages and is diagnosed fairly quickly in 90% of cases. Primary examination with palpation of the tumor and lymphatic drainage zones allows the oncologist to establish a diagnosis. But the morphological examination of the tumor remains mandatory. To treat cancer of the lip, all possible methods of therapy are used: irradiation, medical and surgical methods. The most common type of treatment is radiation therapy, which can be used in the first or second stage of tumor development. Cryodestruction is quite effective, but it is used only at the first stage of the disease. Surgical treatment at an early stage is not used to avoid a significant cosmetic defect.Tip 4: Skin Cancer - How It Looks
Skin cancer is a malignant tumora skin disease that occurs as a result of atypical cell division. There are four types of skin cancer: basal cell, squamous cell, melanoma and adenocarcinoma.
Factors contributing to skin cancer
Among other malignant tumors, cancerSkin is considered a fairly common form of the disease. According to statistics, men can develop skin cancer 1.3 times more often than women. Among the urban population, the intensity of skin cancer is very high and ranks fourth among cancer diseases, second only to cancer of the stomach, breast and lungs. The highest incidence of skin cancer among the population over the age of sixty. Currently, many factors are known that affect the onset of skin cancer. Among them, insolation, the effects of soot and tar, various hydrocarbons and lubricating oils, prolonged contact with tar, arsenic or asphalt, thermal and mechanical injuries, as well as occupational hazards, such as irradiation in the work of an x-ray physician, can be distinguished. The harmful effect of tobacco smoke condensation on the skin has been experimentally proven. Various pathological conditions of the skin, which are attributed to precancerous ones, against which the transformation of normal skin cells into malignant (cancerous) can occur, are the cause of skin cancer. These conditions are divided into obligate progenitors (those that necessarily transform into cancer) and facultative precursors (which do not always translate into cancer). To obligate skin ancestors include diseases of Paget and Bowen, pigment xeroderma and erythroplasia of Keira. To optional include keratoacantham, trophic ulcers, hyper- and dyskeratosis of senile age.Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer, depending on its structure,Is divided into squamous and basal cell types. Basal cell carcinoma accounts for about seventy percent of all cancers of the skin. The distinguishing feature of this kind of skin cancer is its local-destructive growth. And basal cell carcinoma develops from the basal layer of the epidermis. The surface, infiltrative and papillary forms of skin cancer are prominent. Clinical signs of the disease are characterized by the presence of a seal in the form of a gray-yellow plaque, which slowly increases in size, and eventually forms an ulcer with undermined margins and infiltration of surrounding tissues. Ploskocellular cancer can often occur against a background of different precancerous skin diseases. From basal cell, such skin cancer is characterized by faster growth and frequent relapses after treatment. Also squamous cell carcinoma is characterized by metastasis to the lymph nodes, internal organs and bones. Diagnosis of skin cancer is based on carefully collected history, examination, palpation, as well as histological and cytological studies. Since the skin is easily accessible for research, many doctors use the biopsy method to diagnose many skin diseases.Tip 5: Oral leukoplakia: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Leukoplakia of the mouth - changes in mucous membranesshells of a dystrophic nature. The keratinization of the epithelial layer occurs against a background of chronic inflammation and is a reaction to systematic irritation by local factors, smoking, and alcohol. On the background of the disease, the total deficiency of vitamins A and B is diagnosed.

Leukoplakia Symptoms
In the flat form of leukoplakia, the patient feelsUnpleasant symptoms of constriction in the mouth, the mucous membrane becomes cloudy, gradually opalescent and begins to resemble mother of pearl, appearing above the relief.
With a warty form of leukoplakia, the mucous membranes of the oral cavity become uneven and bumpy, and when viewed, large areas of keratinization can be found.
With erosive form, pain occurs, since the entire surface of the oral mucosa is covered with deep ulcers and cracks.
Diagnosis of leukoplakia
From the horny areas of the oral mucosatake a scraping and send it for histological examination to exclude squamous cell carcinoma. Clinical symptoms of leukoplakia of the oral cavity are clearly pronounced. The doctor easily makes the correct diagnosis.
Treatment of leukoplakia
The patient is prescribed a sanation of the oral cavity,recommend abandoning bad habits, taking vitamin A concentrate in droplets three times a day, a course of B vitamins in injections. With warty and erosive form of the disease, the patient is referred for examination to an oncologist, endocrinologist and therapist.







