Tip 1: How to calculate the seasonality factor
Tip 1: How to calculate the seasonality factor
Coefficient seasonality - a value that is taken into account in trade. It allows you to determine the seasonal fluctuations in the speed of selling a particular product. This allows you to organize its delivery on time and do not overstock the warehouse. Calculation and accounting of the coefficient seasonality will optimize the work of the trading company.

Instructions
1
Consider the time periods for calculating the coefficient. For the grocery store as a whole, for the whole year, the monthly sales volume may remain almost unchanged, but if you keep a record for weeks, it will be understood that on Saturdays and Sundays these volumes are much higher than on weekdays. Accordingly, you will need to organize the delivery of perishable goods in a larger volume to the weekend. In stores selling construction materials, the seasonality of sales is expressed in their noticeable increase in the warm season, so the calculation can be done monthly, depending on the month of the calendar year.
2
Keep sales statistics for each type of product. For a reliable result, you must have data for at least two to three years (in the case of a grocery store - in a few weeks). This will allow you not to take into account random factors in your calculations and increase their reliability. Break up all the goods that are sold in your store into categories. Select a unit of measure. It is better not to use money as such - you will constantly have to take into account the Rosstat inflation factor, and it does not always coincide with real indicators. Keep records in the volumes, kilograms, boxes.
3
Use monthly sales data for the latestthree years. To determine the average monthly volume of sales of goods in a certain category, add their indicators for the year and divide by the number of months in the year - 12. Divide the sales by the average to get the ratio seasonality For the given month of the analyzed year. In exactly the same way, calculate the coefficients seasonality For each month in a few years, fold them and divide by the number of years involved in your analysis. You will get an average ratio seasonality. The accuracy of its definition will be the higher, the more years have been analyzed.
Tip 2: How to find the distribution ratio
The main indicator of extraction efficiency is coefficient allocation of. It is calculated by the formula: Co / Cv, where Co is the concentration of the recovered substance in the organic solvent (extractor), and C0 is the concentration of the same substance in the water, after the onset of equilibrium. How can we find the distribution coefficient in an empirical way?

You will need
- - laboratory capacity;
- - a solution of acetic acid;
- - diethyl ferrules;
- - water;
- - cork;
- - a solution of sodium hydroxide;
- - separatory funnel.
Instructions
1
This task is set before you. A solution of acetic acid of known concentration, diethyl ether, test (titrated) alkali-sodium hydroxide solution, as well as a solution of phenolphthalein indicator are given. It is necessary to calculate the distribution coefficient of the substance - acetic acid - between diethyl ether and water. How to do it?
2
In a laboratory container (for example, flat-bottomedFlask with a section), pour a certain volume of acetic acid solution -50 ml. Then add the same volume of diethyl ether in the same flask, close tightly with the "ground" stopper and shake the mixture for several minutes (manually or with a rocking chair).
3
After shaking, take a break for 15 - 20Minutes (you will clearly see how the mixture will exfoliate). Repeat shaking. This procedure should be done at least twice, for more complete extraction of acetic acid and, accordingly, a more accurate result.
4
During the first "upholding", swipecontrol titration of a certain amount of the acid solution with sodium hydroxide solution in the presence of a phenolphthalein indicator. Write down how many milliliters of alkali it took to neutralize, denoting this value of C1.
5
After the last "sedimentation" of the mixture, whena clear interface of the phases will appear, carefully pour into the separatory funnel. After rejecting the lower tap, select a heavier water layer. It still contains acetic acid, but, of course, in a lower concentration - because part of it was extracted by ether.
6
Select exactly the same amount of solutionacid, as in the control titration, and again titrate it with a caustic soda in the presence of phenolphthalein. The number of milliliters of alkali used for neutralization is C2. The distribution coefficient is calculated using the formula: C1 / C2. The problem is solved.
Tip 3: How to calculate the ratio
The importance of mathematics in today's rapidly growingthe developing world is difficult to overestimate. Therefore, it is very important to understand that if you want to achieve success in any branch of modern mathematics, you will have to spend maximum effort and patience. Therefore, the ability to conduct a correct and scientifically based calculation coefficientbut of some mathematical value is a fundamental moment in the formation of the basis of fundamental mathematical knowledge.

Instructions
1
As a rule, any average personbegins acquaintance with the interesting and intriguing world of mathematics from the school bench. Modern school education in our country at the highest level copes with acquaintance of schoolchildren with various branches of modern mathematics. The older the class in the school, the more knowledge base becomes, assessing which it is possible to add the first impression of a person. When calculating the coefficient, you have such input information as long-term liabilities, capitals and assets at the beginning of the reporting period. To learn how to correctly calculate the coefficient of financial activity, read a large number of specialized literature. It is by calculating the ratio of capital and reserves to long-term liabilities.
2
If to explain in other words, then thiscoefficient clearly shows what part of the obligation the enterprise is ready to cover with its reserves, capitals and statutory fund. To get a more realistic picture to date, commitments are made to classify by urgency, and capital - by liquidity. It is also worth noting that you are counting on this important economic indicator for a certain period of the company's work. Taking management decisions, you rely on the dynamics of this coefficient change. Thus, the profitability of your company will increase.
3
When assessing the success of an enterprise,You must rely on the solvency ratio. To calculate it, divide the company's own capital into the total of its balance for a certain period. Knowing this indicator, you will see the specific weight of assets in comparison with its incomes. Thus, it is easy to trace the success and profitability of an enterprise of any industry. Then give a sensible piece of advice to the management of the company. Believe me, it is to appreciate such help with dignity.
Tip 4: How to calculate the seasonality index
The activity of any enterprise is tied toPlanned economic strategy for the production of products or the provision of services. Many companies in the planned indicators include seasonal factors that directly affect the decline and growth in demand for services and products. During planning, it is necessary to take into account such a parameter as the seasonality index.

Instructions
1
Make a list of statistics forseveral recent years. It is necessary to present them in quantitative terms. Do not take data from official statistics, because they do not always accurately describe the real state of affairs.
2
Carry out an analysis of the collected statistics. Remove from the list abnormally small or large values. These data are not part of the statistics and show only one-time major transactions or force majeure circumstances that are uncommon for the operation of the enterprise and the repetition of which is unlikely. In this regard, do not take into account in the statistics random parameters.
3
Decide on the necessary detail. Depending on the scope of the enterprise, this can be a month or a week. For example, if an enterprise sells food, then in the pre-holiday weeks, you can expect an increase in sales, so a week-long account will show a better true state of affairs.
4
Calculate the average amount providedservices or production for each week or month for the selected period of years. Determine the average monthly and average annual volume of services provided or production for the required number of years.
5
Calculate the forecasted seasonality index fora certain month or a week. It is equal to the ratio of the average value of the volume of provision of services or production for the specified number of years for the month sought to the average monthly volume of services or production for a certain number of years. The seasonality index characterizes the percentage of the share of the volume of services or production as compared to the average monthly volume for the year. The seasonality index is used for planning and forecasting the activities of the enterprise for the next year.
Tip 5: How to calculate the amount of goods
The amount of produced or sold goods Is the amount of all products produced for a certain period of time (for example, for the reporting year).

Instructions
1
Determine the amount goods in monetary terms. To do this, multiply its quantity by the cost per unit goods. The calculation can be different if the goods are not homogeneous, and the cost, respectively, varies. In this case, calculate the volume goods For each lot, and then add up all the values.
2
Calculate the volume goods in comparable prices (these are prices for some kind ofa specific year or for a specific date). Such prices can be known or fixed, as well as calculated through certain coefficients (for example, through the level of inflation). In order to find the volume goods in comparable prices, it is necessary to multiply the quantity of all produced products by their value for a certain year. You can also adjust the volume goods at current prices for the required ratio.
3
Find the volume goods, realized for a certain period of time (for a quarter, a year or six months). As a rule, you need to know the values of the residues goods at the end, as well as at the beginning of a given period. Therefore, to determine the volume goods Within a certain period of time, add to the volume of output that was produced during this period, balances goods At the beginning of a given time. Then subtract from the received sum the rests of production which were in a warehouse on the end of necessary term.
4
Calculate the volume of the released goods In money terms as a summation of the finishedproducts, which must be taken for the beginning and end of the reporting period. After that, subtract the amount of the balance of all goods produced for a certain period from the received amount.
5
Determine the amount goods taking into account the work in progress, but which must be launched into production activities. For this, out of the volume goods, Which you need to release this year, subtract the work in progress goods At the beginning of the period. Further, from the received value subtract the amount of work in progress at the end of the period.
Tip 6: How to calculate the reliability
To compare two samples taken from onegeneral population, or two different states of the same population, the Student method is used. Using it, you can calculate the reliability of the differences, that is, find out whether you can trust the measurements.

Instructions
1
In order to choose the correct calculation formulaDetermine the size of the sample groups. If the number of measurements is greater than 30, such a group will be considered large. Thus, three options are possible: both groups are small, both groups are large, one group is small, the second is large.
2
In addition, you will need to know whetherMeasurements of the first group with measurements of the second. If each i-th version of the first group is opposed to the i-th version of the second group, then they are called pairwise-dependent. If the variants within the group can be interchanged, such groups are called groups with pairwise-independent variants.
3
To compare groups with pairwise independentVariants (at least one of them must be large), use the formula shown in the figure. Using the formula, you will be able to find the Student's criterion, it is from this that the confidence probability of the difference between the two groups is determined.

4
To determine the Student's test for groupsSmall size with pairwise-independent options, use another formula, it is presented in the second figure. The number of degrees of freedom is calculated in the same way as in the first case: add up the volumes of two samples and subtract the number 2.

5
Compare two small groups with pairwise-dependent results by using two formulas, of your choice. In this case, the number of degrees of freedom is calculated differently, according to the formula k = 2 * (n-1).
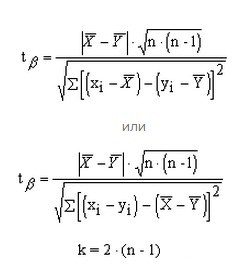
6
Next, determine the confidence probability byStudent's t-criteria table. In this case, consider that the sample was reliable, the confidence probability should be at least 95%. That is, find the value of the number of degrees of freedom in the first column, and in the first line - the calculated Student's criterion and estimate, less or more, the 95% probability obtained.
7
For example, you got t = 2.3; k = 73. According to the table, determine the confidence probability, it is more than 95%, therefore, the differences in the samples are reliable. Another example: t = 1.4; k = 70. According to the table, in order to obtain a minimum confidence value of 95%, for k = 70, t should be at least 1.98. At you it it is less - only 1,4, therefore distinction of samples is doubtful.







